ELUSIVE HERPES | Herpes Virus Treatment
Most of us are aware that in adulthood, about 95% of the world's population will somehow be infected with herpes type 1 or 2. Epstein Barr's virus (which belongs to herpes type 4) will co-infect 70% of the world's population. Cytomegalovirus (or herpes type 5) - 30-49% of the population. Most of us have heard that it makes sense to treat only acute herpetic infection, mononucleosis, or in persons with acquired immunodeficiencies. But few people are aware that the chronic persistent herpetic infection, with periods of exacerbation and viral reactivation, is itself may be the cause for secondary immunodeficiency, and chronic persistence of HSV and HHV2 are both linked to progression of dementia and Alzheimer's disease. In pregnant women and in woman preparing to become a mother, with chronic persistent herpetic infection and frequent viral reactivation, the likelihood of premature pregnancy termination and the birth of a child later diagnosed within the ASD and developmental disabilities, increases. Chronic persistence of herpes type 6 and EBV is associated with chronic fatigue syndrome, chronic persistence of therpes type 8 - with Kaposi's sarcoma, and cancer
Transmission of herpes viruses:
• Occurs through body fluids and excretions: blood, urine, saliva, lacrimal fluid, breast milk, amniotic fluid, semen, vaginal discharge, via tissues and organs - transplants.
• Transmission from pregnant woman to fetus, from mother -to child, from one sexual partner to another, through handshakes and household items, airborne way.
• Another mechanism is blood transfusion: blood components that contain infected white blood cells, or organ transplants from seropositive donors.
In children infected intrauterine, neurological symptoms can be observed: motor syndrome disorders, hydrocephalic syndrome.
And at birth, in this category of children signs of delayed brain development frequently found.
- More severe neurological changes were detected in children with combined infection with herpes simplex viruses andCMV
-On MRI of the brain in children of 1 month of life, infected in utero by CMV or EBV,ischemicchanges in the periventricular zones can be found.
- EBV infectionsuppresses the T cellular line of immunity and increases B cells production.
- CMV infection causes T cells decrease, increase in activated T killer cells, which indicates intensity of reactions.
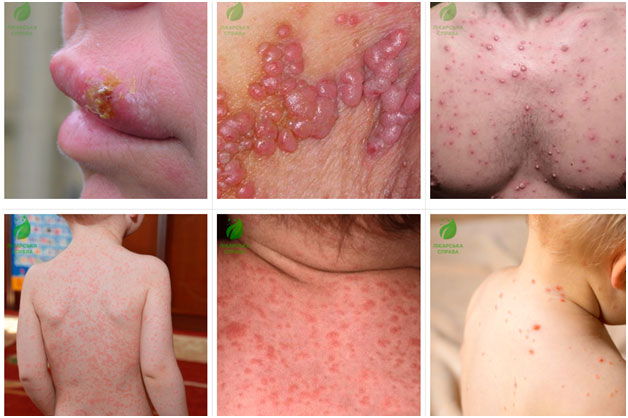
Diagnostic tools and material for research: -
Sputum, urine, saliva, spinal fluid, throat swab, nasopharyngeal swab: forviral DNA detection by PCR.
-Blood serum, lymphocytes, or leukocytes: Immunoglobulins class M can be detected in blood serum within 4-6 days, maximum within 15-20 days. Specific IgG and IgA: on days 10-14 and can persist for 1-3 months.
-Blood serum specificIgG can last for life, nevertheless it is important to compare the titer of specific IgG in order to understand the likelihood ‘behaviour’ of this chronic infection: is it in dormant state(if specific IgG stays unchanged), or persistent infection is reactivated (if titer of IgG is increasing).
A smart reader will ask: eventually, should we treat or to not treat a chronic herpes infection?
Of course, there is no universal answer to this question.
But in each specific case, it is necessary to consider the patient clinical symptoms, existing complaints, to determine the presence or absence the signs of chronic viremia, signs of viral reactivation.
In acute cases and in cases of frequent viral reactivation, the treatment protocol will consist of antiviral drugs:
-Medications such as Acyclovir, Valtrex, Ganciclovir, etc. -Immunotropics: Interferon alpha 2 b, interferon stimulants,T cell immunity stimulants or suppressors, -
- If necessary: Intravenous immunoglobulins
- Herbal remedies, vitamins, and supplements: Cryptolepis, Cat’s Claw, Monolaurin, Lysine, Zinc, Vit D, Ascorbic acidetc.
In our medical centre we will find the best treatment solution for you, create personalised diagnostic and treatment protocol.


